Xanthomonas (genus)
| Literature database |
|---|
| 2046 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of antagonists |
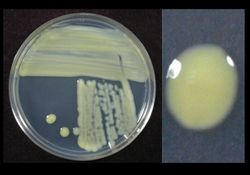
Source: NC State University Plant Pathology Laboratory - (Wikimedia Commons)
Xanthomonas Dowson 1939
The genus includes a large number of plant pathogens, several causing serious diseases. The species of Xanthomonas are Gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria, about ½-1 µm long. They produce a non-diffusible yellow pigment on growth media. They do not have a resting stage and some have a single polar flagellum. Usually they are catalase positive and oxidase negative.
Previously, pathovars and species have been described on the basis of their host plants and symptoms. This system has been replaced by a classification based on the structure of the 16S ribosomal DNA. The plant diseases caused include canker diseases (e.g. citrus canker), blight diseases (e.g. bacterial blight of rice) and rots (e.g. black rot of crucifers).
For a taxonomic review of Xanthomonas see Constantin et al. (2016), see also Vauterin et al. (2000).
Currently, the following species have been entered into the system:
- Xanthomonas albilineans
- Xanthomonas arboricola
- Xanthomonas axonopodis
- Xanthomonas campestris
- Xanthomonas cassavae
- Xanthomonas citri
- Xanthomonas citri pv. glycines
- Xanthomonas citri pv. mangiferaeindicae
- Xanthomonas citri pv. viticola
- Xanthomonas citri subsp. malvacearum
- Xanthomonas cucurbitae
- Xanthomonas euvesicatoria
- Xanthomonas fragariae