Diplodia (anamorphic genus)
From Pestinfo-Wiki
| Literature database |
|---|
| 392 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of antagonists |
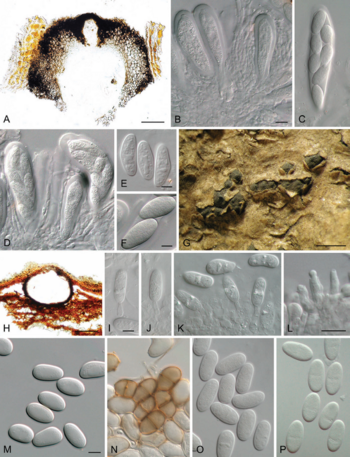
Diplodia mutila - A) sectioned ascoma; B) immature asci and pseudoparaphyses; C, D) asci with ascospores; E, F) ascospores; G) conidiomata partially erumpent through host; H) sectioned conidioma; I–L) conidiogenous cells; M–P) conidia. Scale bars: A = 100 μm, B = 10 μm, E, F = 10 μm, G = 500 μm, H = 100 μm, I, L = 10 μm, M = 10 μm. Scale bar in B applies to C, D. Scale bar in I applies to J, K. Scale bar in M applies to N–P.
Author(s): A.J.L. Phillips, A. Alves, J. Abdollahzadeh, B. Slippers, M.J. Wingfield, J.Z. Groenewald and P.W. Crous
Source: Studies in Mycology, 2013, 76, p.92
Author(s): A.J.L. Phillips, A. Alves, J. Abdollahzadeh, B. Slippers, M.J. Wingfield, J.Z. Groenewald and P.W. Crous
Source: Studies in Mycology, 2013, 76, p.92
Diplodia Fr. 1834
This genus of ascomycetes contains several important plant pathogens like the type species, Diplodia mutila. They are widespread and cause dieback and canker diseases on trees and other woody crops.
The genus is characterized by several morphological features, as well as the DNA structure of its members. E.g. the conidia are initially hyaline, aseptate and thick-walled. They often become 1–2-septate and pale transluscent brown after discharge from the pycnidia, but the change in the colouration can be delayed or never occurs.
Type species: Diplodia mutila
For a taxonomic review see Phillips et al., 2013.
Currently, the following species have been entered into the system: