Diplodia mutila
From Pestinfo-Wiki
| Literature database |
|---|
| 86 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
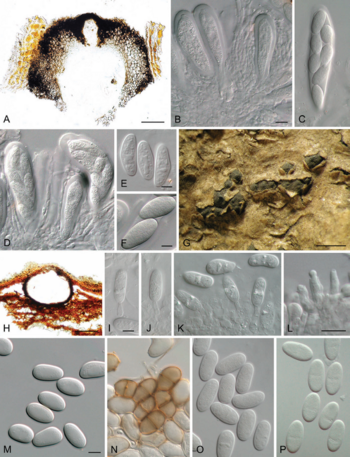
Diplodia mutila - A) sectioned ascoma; B) immature asci and pseudoparaphyses; C, D) asci with ascospores; E, F) ascospores; G) conidiomata partially erumpent through host; H) sectioned conidioma; I–L) conidiogenous cells; M–P) conidia. Scale bars: A = 100 μm, B = 10 μm, E, F = 10 μm, G = 500 μm, H = 100 μm, I, L = 10 μm, M = 10 μm. Scale bar in B applies to C, D. Scale bar in I applies to J, K. Scale bar in M applies to N–P.
Author(s): A.J.L. Phillips, A. Alves, J. Abdollahzadeh, B. Slippers, M.J. Wingfield, J.Z. Groenewald and P.W. Crous
Source: Studies in Mycology, 2013, 76, p.92
Author(s): A.J.L. Phillips, A. Alves, J. Abdollahzadeh, B. Slippers, M.J. Wingfield, J.Z. Groenewald and P.W. Crous
Source: Studies in Mycology, 2013, 76, p.92
Diplodia mutila (Fr. 1823) Mont. 1834
The fungus causes dieback and canker on oak and other trees or grapevine in Europe, South Africa and North America. The conidia are hyaline, aseptate, smooth, thick-walled, oblong to ovoid, straight on both ends and broadly rounded. Unlike other species of this genus, they rarely becoming pale brown and septate with age. The conidia are on average 25 x 13 µm large.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Diplodia-Rindenbrand |
| • English: | canker/dieback of oak black dead-arm disease of grapevine |
| • Français: | dead-arm noir de la vigne |
Synonyms:
Botryosphaeria stevensii
Physalospora mutila
- Other images of Diplodia mutila (Wikimedia Commons and IPM Images - click to enlarge)


