Colletotrichum lupini
| Literature database |
|---|
| 29 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
Colletotrichum lupini (Bondar) Damm, P.F. Cannon & Crous 2012 - (lupin anthracnose)
The fungus has a world-wide distribution and is a seed-borne disease of lupin. It can survive on infected seeds for up to 2 years and also persists on the stubble of the crop. Under wet and warm conditions, one in 1000 infected seeds may result in an epidemic and yield losses of up to 50%. Infections and conidia production follow a rapid cycle and the fungus readily spreads by rain splashes. Symptoms include oval shaped lesions and bending of infected stems like a shepherd’s crook. Control involves resistant varieties and the use of disease-free seeds. However, new infections might spread from wild lupins.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Anthraknose der Lupine Brennfleckenkrankheit der Lupine |
| • English: | lupin anthracnose |
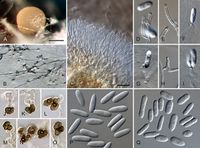
Conidia are smooth-walled, aseptate, straight and cylindrical, with one end rounded and one end acute. They measure approximately 10-15 x 4-5 µm. Cultures are gray with orange spots and usually do not produce setae.
For a review see Talhinhas et al., 2016.
Synonyms:
Gloeosporium lupini
- Other images of Colletotrichum lupini (Open Media and Studies in Mycology - click to enlarge)