Botryosphaeria (genus)
From Pestinfo-Wiki
| Literature database |
|---|
| 272 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of antagonists |
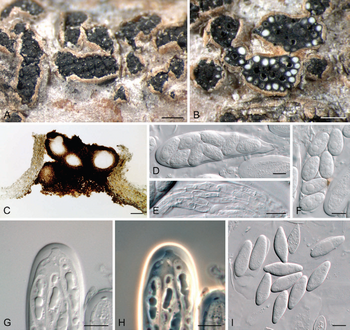
Botryosphaeria dothidea - A) botryose cluster of conidiomata erumpent through the bark of a poplar twig; B–E) conidiogenous cells with periclinal thickenings (black arrowheads) or annellations (white arrowheads); F) paraphyses; G, H) conidia; I) spermatia; J) pigmented, thick-walled, septate conidia. Scale bars: A = 0.5 mm, B–J = 10 μm.
Author(s): A.J.L. Phillips, A. Alves, J. Abdollahzadeh, B. Slippers, M.J. Wingfield, J.Z. Groenewald and P.W. Crous
Source: Studies in Mycology, 2013, 76, p.75
Author(s): A.J.L. Phillips, A. Alves, J. Abdollahzadeh, B. Slippers, M.J. Wingfield, J.Z. Groenewald and P.W. Crous
Source: Studies in Mycology, 2013, 76, p.75
Botryosphaeria Ces. & De Not. 1863
This genus of ascomycetes contains several important plant pathogens like the type species Botryosphaeria dothidea. These are widespread and cause diseases like cankers, dieback, fruit rot, stem-end rot and shoot blight on woody crops. The genus is characterized by several morphological features, as well as the DNA structure of its members. E.g. the ascospores are hyaline and aseptate. However, they can become pale brown and septate with age.
Type species: Botryosphaeria dothidea
For a taxonomic review see Phillips et al., 2013.
Currently, the following species have been entered into the system: