Grapevine leafroll-associated virus 3
| Literature database |
|---|
| 217 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |

Author(s): Hans J. Maree1, Rodrigo P.P. Almeida, Rachelle Bester, Kar Mun Chooi, Daniel Cohen, Valerian V. Dolja, Marc F. Fuchs, Deborah A. Golino, Anna E. C. Jooste, Giovanni P. Martelli, Rayapati A. Naidu1, Adib Rowhani, Pasquale Saldarelli and Johan T. Burger
Source: Front. Microbiol. (2013) 4:82
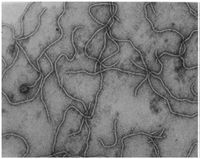
Grapevine leafroll-associated virus 3 (GLRaV-3)
The virus belongs to a series of viruses associated with the grapevine leafroll disease. It causes a widespread, graft-transmitted disease which affects grape yield and quality. It can also by transmitted by various species of mealybugs like Planococcus citri, Planococcus ficus or Pseudococcus longispinus. The symptoms vary according to grapevine cultivar and temperature and include pronounced leaf-rolling by harvest time (mainly in white grape varieties) or interveinal reddening while most veins remain green (mainly in red grape varieties). Sometimes no apparent symtoms are visible.
Management can be achieved by using certified, virus-free stocks, maximizing the distance between new plantings and old virus-infected vines, minimizing contact of farming tools with infected vines and screening for virus infections and removing infected plants. The use of insecticides to control insect vectors has not always been effective.
GLRV-3 particles are flexuous and very long filaments, 1,800 × 12 nm in size, with cross bands. The genome consists of mono-partite, positive-strand RNA with about 18,500 nucleotides.
For a review see Maree et al., 2013.
- Other images of Grapevine leafroll-associated virus 3 (from Front. Microbiol. - click to enlarge)