Maintenance
All wikis at Biowikifarm are in read-only mode due to the restoration after a severe cyberattack in October 2023.
After 1 year being shut down the Biowikifarm is online again.
You see the latest restored version from 18th October 2023.
Difference between revisions of "Dendroctonus frontalis"
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TaxLinks|LnkDendroctonus}} | {{TaxLinks|LnkDendroctonus}} | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{LiteratureDBX|{{PAGENAME}}|753|browse,Ccountrylnk,Pcrops,AbenefialsN}} |
[[File:Dendroctonus_frontalis_IPM5289031.jpg|250px|thumb|''Dendroctonus frontalis'' - mounted adult (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Author: Erich G. Vallery, USDA Forest Service<br/>Source: [http://www.ipmimages.org/browse/detail.cfm?imgnum=5289031 IPM images]]] | [[File:Dendroctonus_frontalis_IPM5289031.jpg|250px|thumb|''Dendroctonus frontalis'' - mounted adult (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Author: Erich G. Vallery, USDA Forest Service<br/>Source: [http://www.ipmimages.org/browse/detail.cfm?imgnum=5289031 IPM images]]] | ||
| − | '''''<font color="#800000">Dendroctonus frontalis</font>''''' Zimmermann (southern pine beetle) | + | '''''<font color="#800000">Dendroctonus frontalis</font>''''' Zimmermann , 1868 - (southern pine beetle) |
| − | The beetle is a major pest of pine forests in North America. Populations undergo cyclic fluctuations every 7-12 years. The beetle introduces a pathogenic blue-stain fungus (''[[Ophiostoma minus]]'') into the trees which blocks water movement. During outbreaks, mass aggregations are initiated by pheromones like frontalin. The beetles bore into the bark and feed on the phloem. The outbreak areas are characterized by scattered pockets of dead and dying trees. | + | The beetle is a major pest of pine forests in parts of North and Central America. In North America, mainly southern and southeastern parts are affected. Populations undergo cyclic fluctuations every 7-12 years. The beetle introduces a pathogenic blue-stain fungus (''[[Ophiostoma minus]]'') into the trees which blocks water movement. During outbreaks, mass aggregations are initiated by pheromones like frontalin. The beetles bore into the bark and feed on the phloem. The outbreak areas are characterized by scattered pockets of dead and dying trees. |
{{VN | {{VN | ||
|en=southern pine beetle | |en=southern pine beetle | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|fr=dendroctone méridional du pin | |fr=dendroctone méridional du pin | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | For a review of outbreaks see [[Forests (2020) 11 (2 - 173)|Gomez et al. (2020)]], for other details see the respective page in the [[bugwood:Dendroctonus_frontalis|BugwoodWiki]]. | |
| − | For details see the respective page in the [[bugwood: | + | |
Latest revision as of 19:22, 14 October 2022
| Literature database |
|---|
| 167 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of natural enemies |

Author: Erich G. Vallery, USDA Forest Service
Source: IPM images
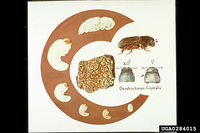
Dendroctonus frontalis Zimmermann , 1868 - (southern pine beetle)
The beetle is a major pest of pine forests in parts of North and Central America. In North America, mainly southern and southeastern parts are affected. Populations undergo cyclic fluctuations every 7-12 years. The beetle introduces a pathogenic blue-stain fungus (Ophiostoma minus) into the trees which blocks water movement. During outbreaks, mass aggregations are initiated by pheromones like frontalin. The beetles bore into the bark and feed on the phloem. The outbreak areas are characterized by scattered pockets of dead and dying trees.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • English: | southern pine beetle |
| • Español: | escarabajo de pino sureño |
| • Français: | dendroctone méridional du pin |
For a review of outbreaks see Gomez et al. (2020), for other details see the respective page in the BugwoodWiki.
- Other images of Dendroctonus frontalis (IPM Images and PaDIL - click to enlarge)