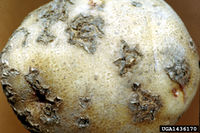
Streptomyces scabiei
| Literature database |
|---|
| 168 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of antagonists |

Source: Wikimedia Commons
Streptomyces scabiei (ex Thaxter 1891) Lambert and Loria, 1989 - (potato scab)
The bacterium causes a widespread and important disease of potatoes which has been also reported from some other root crops. The Gram-positive bacterium is soil-borne and infects the tubers through small wounds, causing corky lesions. The lesions may be superficial, raised or sunken, depending on the potato variety. The disease spreads mechanically or through rain splashes and seed potatoes. Although it is a bacterium, it forms small, branched, fungi-like hyphae and has a large genome. The hyphae also develop chains of cylindrical spores, each about 1 x ½ µm large. Spore-bearing hyphae can have special spiral structures. Hyphae and spores overwinter in the soil. Resistant varieties, disease-free seed potatoes and crop rotation are recommended for control. The disease is not found in soils with a low pH (but see Streptomyces acidiscabies).
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Kartoffelschorf |
| • English: | potato scab |
| • Français: | gale de la pomme de terre |
Synonyms
Streptomyces scabies
For details see the respective page in Wikipedia.
- Other images of Streptomyces scabiei (Wikimedia Commons and IPM Images - click to enlarge)