Puccinia polysora
| Literature database |
|---|
| 39 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
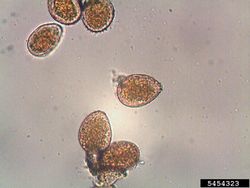
Puccinia polysora Underw. 1897 - (southern corn rust)
This fungus is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions and causes a rust disease of maize. Several other grasses can also become infected. P. polysora is often the most important rust disease of maize with the disease progressively worsening as the plant develops. The symptoms consist of small uredial pustules on the leaf surfaces, up to 2 mm in diameter. They are orange to brownish and mainly develop on the upper surface of the lower leaves. Infections result in necrosis and often significant yield losses. Losses of up to 50% have been reported. The urediniospores are around 30 µm long and slightly elongated. They spread through the wind and the fungus can survive on plant debris. Management relies mainly on crop rotation and resistant cultivars.
Puccinia sorghi is another important rust disease of maize and both diseases are not always easy to distinguish by symptoms and spore morphology (Crouch and Szabo, 2011). The urediniospores of Puccinia sorghi are rounder and develop on both the upper and lower leaf surfaces.