Phytophthora plurivora
| Literature database |
|---|
| 75 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of antagonists |

Authors: T. Jung and T.I. Burgess
Source: Persoonia (2009), vol. 22 p. 96
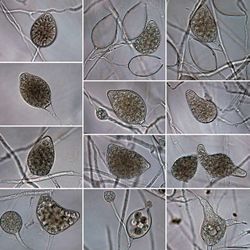
Authors: T. Jung and T.I. Burgess
Source: Persoonia (2009), vol. 22 p. 103
Phytophthora plurivora T. Jung & T.I. Burgess 2009
This oomycete is wide-spread, highly aggressive and infects various, mainly woody host plants like forest trees. It has been reported from North America and Europe since the 1990s, initially mainly from nurseries, and appears to be a recent introduction there. On the other hand, it had been misidentified in Western Australia for around 30 years as Phytophthora citricola, a closely related species.
The species causes dieback of shoots and crowns, small-sized and often yellowish foliage, extensive fine root losses, root lesions, collar rots and aerial cankers. It is homothallic with paragynous antheridia, semipapillate persistent sporangia, does not form catenulate hyphal swellings and has a growth optimum around 25 °C, see Jung and Burgess, 2009.