Phoma (anamorphic genus)
| Literature database |
|---|
| 29 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
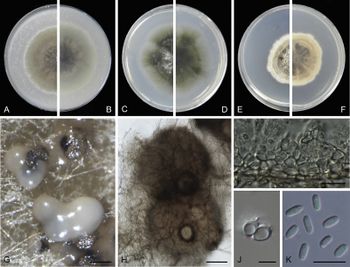
Author(s): Q. Chen, J.R. Jiang, G.Z. Zhang, L. Cai and P.W. Crous
Source: Studies in Mycology (2015) 82, p. 199
Phoma Sacc. 1880, emend. Boerema & G.J. Bollen
The genus is widespread and several hundred species with many plant pathogens have been assigned to it. These cause mainly leaf spot diseases. Other species are saprophytes or endophytes and some are even human pathogens or live in the marine environment.
Previously, species were described, based on morphological characters. The structure of the conidia, pycnidia and other features have been also used to divide the genus into several sections (groups). While some of these sections are still recognized, the genus is now mainly defined by the molecular structure of 3 genes, the internal transcribed spacers region of the rDNA, the actin gene and cytochrome c oxidase subunit I. It has been revised repeatedly since 2004 and several new genera have been created or re-created using previous Phoma species, e.g.:
Type species: Phoma herbarum.
For a review and reorganization of the genus see Aveskamp et al., 2010 as well as de Gruyter et al., 2013.
Currently, the following species have been entered into the system: