Neocosmospora ipomoeae
From Pestinfo-Wiki
| Literature database |
|---|
| 8 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
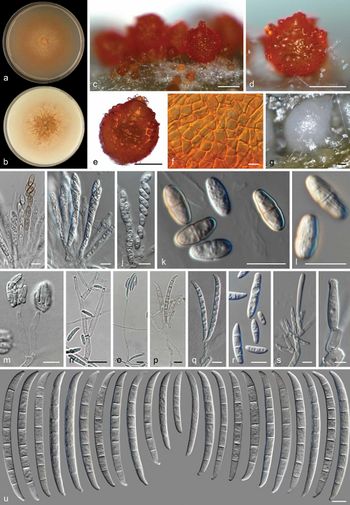
Neocosmospora ipomoeae - a+b) cultures, c-e) perithecia, f) detail of peridium cells, g) sporodochia, h-j) asci, k-l) ascospores, m-q) aerial conidiophores, r) aerial conidia, s-t) sporodochial conidiophores and phialides, u) sporodochial conidia - scale bars: c–e, g = 100 μm; all others = 10 μm (click on image to enlarge it)
Author(s): M. Sandoval-Denis, L. Lombard and P.W. Crous
Source: Persoonia (2019), 43, p. 135
Author(s): M. Sandoval-Denis, L. Lombard and P.W. Crous
Source: Persoonia (2019), 43, p. 135
Neocosmospora ipomoeae (Halst.) L. Lombard & Crous 2015
This fungus is widely distributed and infects eggplants, tomatoes, green pepper, ornamentals and other crops like passionfruit or Panax. It causes stem rot, dieback, wilts and other diseases, often leading to plant death. The initial symptoms on tomatoes are water-soaked lesions on the lower stems, near the collar which later turn brown. N. ipomoeae is homothallic and forms abundant orange-brown perithecia both on artificial media as well as in the lesions on diseased plants (Kwon et al., 2017).
Synonyms:
Haematonectria ipomoeae
Nectria ipomoeae
Fusarium solani var. striatum (doubtful)
Fusarium striatum (doubtful)
For a taxonomic review see Sandoval-Denis et al. (2019).