Xylella fastidiosa
| Literature database |
|---|
| 597 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of antagonists |

Source: Wikimedia Commons
Xylella fastidiosa Wells et al. 1987
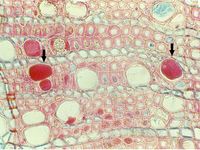
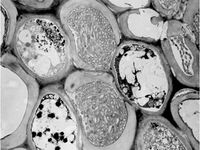
This species is a Gram-negative bacterium which infects the xylem of certain plants, causing diseases like citrus variegated chlorosis, Pierce's disease of grapevine or leaf scorch of almond, coffee, pear, pecan and other trees. It is wide-spread in tropical and subtropical parts of the Americas and since 2013 has been also reported from several regions in Europe and Asia. Symptoms include scorching of the leaves, yellowing, stunting, dwarfing, die-back and the development of small fruits, depending on the host plant. The symptoms often resemble drought effects. Leaf scorch, the main symptom, affects the marginal parts of the leaves which dry off and are separated from the green leaf areas by a yellow margin. A large number of hosts have been recorded and different subspecies have been described which appear to be specialised on a smaller group of host plants and often have a more restricted distribution.
Distribution and introductions
Reports from subtropical parts of North America (e.g. California on grapevine) and South America (e.g. southern Brazil on citrus) are most common. Several forms are suspected to have been introduced in the past from South to North America and vice versa.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Pierce-Krankheit |
| • English: | citrus variegated chlorosis pecan bacterial leaf scorch plum leaf scald phony peach disease Pierce's disease of grapes almond leaf scorch leaf scorch of pecan leaf scald of plum leaf scorch of almond |
| • Français: | maladie de Pierce du raisin échaudure bactérienne des feuilles |
| • Português: | clorose variegada dos citros |
In 2013, X. fastidiosa was reported from grapevine in Taiwan and from olive in Italy (Martelli et al., 2016). In 2014, the pathogen was reported from grapevine and almond trees in Iran.
Since 2015, several forms of the bacterium have been reported from France where it infects mainly the ornamental shrub Polygala myrtifolia. In 2016 an infected cherry tree was found in the Balearic Islands (Spain) and infected oleander plants were reported from Germany. Since 2017, the typical form infecting grapevine (Pierce's disease) has been reported from Mallorca, Spain. Attempts have been and are being made to eradicate new introductions which are apparently caused by the import of infected plant material.
Biology and transmission
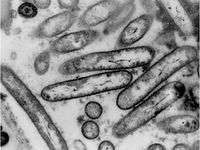
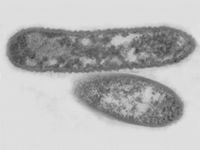
The bacterium can be cultured on artificial media but grows very slowly. It has a rod-shaped form, about 1-3 µm long, and has pili (hair-like extensions) on its surface. While the bacterium can easily move upwards with the xylem fluid of the plant, the pili also enable the bacterium to move slowly downwards.
X. fastidiosa is transmitted by a variety of xylem feeding leafhoppers (Cicadellidae) and also by some species of froghoppers (Cercopidae). For example, the glassy-winged sharpshooter, Homalodisca vitripennis, transmits Xylella fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa causing Pierce’s disease of grapevine in southwestern North America. The bacteria attach themselves to the foregut wall of the leafhopper vector and are passed back into the xylem with the saliva of the vector. For reviews on the insect transmission of this disease agent see Krugner et al. (2019) and Overall and Rebek (2017).
Management
Management of the disease has proven difficult. Providing plants with enough moisture, e.g. through mulching, can delay the disease development. Also using resistant cultivars has shown some promise. Since many regions are free from the disease, quarantine procedures are of particular importance for confining the pathogen.
Subspecies
Forms of X. fastidiosa that cause citrus variegated chlorosis and Pierce's disease of grapevine are among the most destructive varieties of the bacterium. Various other subspecies have been also described as listed below.
- Xylella fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa - infects grapevine and other trees, causing Pierce's disease
- Xylella fastidiosa subsp. morus - infects mulberry
- Xylella fastidiosa subsp. multiplex - infects peach, elm, plum, sycamore, almond, pecan and olive
- Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca - infects citrus, coffee and olive, introduced into Italy and France
- Xylella fastidiosa subsp. piercei - infects grapevine, alfalfa, almond and maple
- Xylella fastidiosa subsp. sandyi - infects oleander, causing oleander leaf scorch, introduced into France
- Xylella fastidiosa subsp. tashke - causes leaf scorch on Chitalpa tashkentensis trees
For a review and diagnostic procedures see the respective EPPO datasheet (2019).
- Other images of Xylella fastidiosa (Wikimedia Commons, PaDIL and IPM Images - click to enlarge)