Puccinia striiformis
| Literature database |
|---|
| 790 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of antagonists |
Puccinia striiformis Westend. 1854 - (stripe rust)
The fungus causes a serious disease of wheat in temperate regions and is found in almost all areas where wheat is grown. Yield losses can exceed 50% in susceptible varieties. Other cereals (especially barley) and grasses can also become infected.
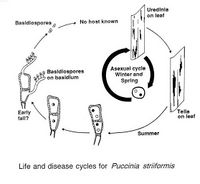
The disease is characterized by the yellow to orange spore pockets being arranged in long and narrow stripes on the leaves, usually between the veins. These produce urediniospores which can be carried by the wind over hundreds of kilometres. They germinate readily under moist conditions. Black telia are produced at the end of the growing season. For a review on the epidemiology of the pathogen see Chen (2005).
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Gelbrost Streifenrost |
| • English: | stripe rust yellow rust wheat stripe rust |
| • Español: | roya amarilla roya anaranjada |
| • Français: | rouille jaune du blé rouille striée du blé |
Puccinia species often have Berberis (barberry) plants as alternate (or aecial) hosts. Although natural infections of Berberis by P. striiformis have not yet been observed in the field, they can be artificially produced.
The disease is mainly managed through the use of resistant cultivars and more than 50 resistant genes haves been identified.
Urediniospores have a size of 24 x 20 µm, are covered with spines on the surface and have 6–18 scattered germ pores. Teliospores are approximately 35-50 x 18 µm large and two-celled, the basidiospores 11 x 7 µm.
Closely related species are
Puccinia pseudostriiformis on Poa
Puccinia striiformoides on Dactylis, and
Puccinia gansensis on Achnatherum.
Synonyms:
Puccinia glumarum
For a review see Chen et al. (2014).
- Other images of Puccinia striiformis (Wikimedia Commons, PaDIL and IPM Images - click to enlarge)