Phytophthora cryptogea
| Literature database |
|---|
| 131 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of antagonists |
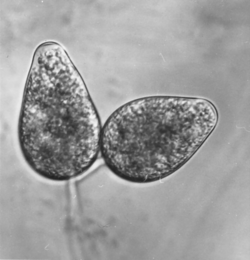
Phytophthora cryptogea Pethybr. & Laff 1919
The oomycete is a widespread and soil-borne oomycete pathogen which causes root and foot-rot on ornamentals, vegetables and many other crops. Infections often result in plant death and substantial yield losses. Symptoms include blight, wilting, chlorosis, dieback and/or stunting. Roots are primarily infected, but the pathogen quickly spreads to other parts of the plant. The sporangia and zoospores readily disperse in irrigation water, in hydroponic cultures and during floods. The zoospores are the main source of new infections. For control fungicides (like phosphite) and plant resistance have been used.
P. cryptogea is morphologically very similar to P. drechsleri. In cultures it has a lower optimal growth temperature (22-25°C compared to 28-31° C for P. drechsleri). Sporangia are oval to pyriform, approximately 40 x 30 µm large. Chlamydospores are rare. Oospores have a diameter of about 22-23 µm. P. cryptogea is heterothallic, but some homothallic isolates have been described.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Wurzelfäule der Tomate |
| • English: | foot rot of tomato |
| • Français: | pourriture du collet des plantes d'ornement |