Difference between revisions of "Therioaphis trifolii"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{TaxLinks|LnkTherioaphis}} |
| − | {{ | + | {{LiteratureDBX|{{PAGENAME}}|838|browse,Ccountrylnk,Pcrops,AbenefialsN}} |
[[File:Therioaphis_trifolii_PaDIL136143a.jpg|250px|thumb|''Therioaphis trifolii'' apterous vivipara (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Author(s): Simon Hinkley & Ken Walker, Museum Victoria<br/>Source: [http://www.padil.gov.au/pests-and-diseases/Pest/Main/136143 PaDIL]]] | [[File:Therioaphis_trifolii_PaDIL136143a.jpg|250px|thumb|''Therioaphis trifolii'' apterous vivipara (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Author(s): Simon Hinkley & Ken Walker, Museum Victoria<br/>Source: [http://www.padil.gov.au/pests-and-diseases/Pest/Main/136143 PaDIL]]] | ||
| − | <font color="#800000">'''''Therioaphis trifolii'''''</font> (Monell, 1882) - (spotted alfalfa aphid) | + | <font color="#800000">'''''Therioaphis trifolii'''''</font> (Monell, 1882) - (spotted alfalfa aphid) |
| − | + | ||
| − | The aphid is about 1½ mm long and yellowish–green, with four to six rows of dark spots running along the length of its back. It causes veinal chlorosis and | + | The aphid is native in Europe and the Mediterranean region and has spread to other regions like North America (1950's) and Australia (1977), as well as to South Africa, Japan and New Zealand (all around 1980). In the invaded countries, it has become a serious pest of alfalfa, causing extensive damage. In Australia, control was achieved through resistant varieties and the introduction of a parasitic wasp from Iran. However, new outbreaks were recorded there since 1989 by a genetically distinct biotype, known as the spotted clover aphid. |
| + | {{VN | ||
| + | |de=Luzerneblattlaus | ||
| + | |en=spotted alfalfa aphid<br/>spotted clover aphid<br/>yellow clover aphid | ||
| + | |fr=puceron de la luzerne | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | The aphid is about 1½ mm long and yellowish–green, with four to six rows of dark spots running along the length of its back. It causes veinal chlorosis and sooty mold due to honeydue excretion. It can transmit viruses like the [[Alfalfa mosaic virus]] or [[Cucumber mosaic virus]]. | ||
'''Synonyms:'''<br/> | '''Synonyms:'''<br/> | ||
| Line 11: | Line 16: | ||
''Therioaphis trifolii forma maculata'' | ''Therioaphis trifolii forma maculata'' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<gallery widths=200px caption="Other images of Therioaphis trifolii (PaDIL - click to enlarge)"> | <gallery widths=200px caption="Other images of Therioaphis trifolii (PaDIL - click to enlarge)"> | ||
| + | File:Therioaphis maculata IPM5512071.png | ||
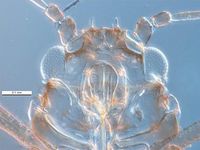
File:Therioaphis_trifolii_PaDIL136143b.jpg|apterous vivipara, head | File:Therioaphis_trifolii_PaDIL136143b.jpg|apterous vivipara, head | ||
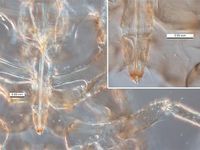
File:Therioaphis_trifolii_PaDIL136143c.jpg|apterous vivipara, rostrum | File:Therioaphis_trifolii_PaDIL136143c.jpg|apterous vivipara, rostrum | ||
Latest revision as of 21:49, 25 August 2022
| Literature database |
|---|
| 76 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of natural enemies |

Author(s): Simon Hinkley & Ken Walker, Museum Victoria
Source: PaDIL
Therioaphis trifolii (Monell, 1882) - (spotted alfalfa aphid)
The aphid is native in Europe and the Mediterranean region and has spread to other regions like North America (1950's) and Australia (1977), as well as to South Africa, Japan and New Zealand (all around 1980). In the invaded countries, it has become a serious pest of alfalfa, causing extensive damage. In Australia, control was achieved through resistant varieties and the introduction of a parasitic wasp from Iran. However, new outbreaks were recorded there since 1989 by a genetically distinct biotype, known as the spotted clover aphid.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Luzerneblattlaus |
| • English: | spotted alfalfa aphid spotted clover aphid yellow clover aphid |
| • Français: | puceron de la luzerne |
The aphid is about 1½ mm long and yellowish–green, with four to six rows of dark spots running along the length of its back. It causes veinal chlorosis and sooty mold due to honeydue excretion. It can transmit viruses like the Alfalfa mosaic virus or Cucumber mosaic virus.
Synonyms:
Therioaphis maculata
Therioaphis trifolii forma maculata
- Other images of Therioaphis trifolii (PaDIL - click to enlarge)