Difference between revisions of "Frankliniella schultzei"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
}} | }} | ||
For control, insecticides are predominantly used. However, temporary flooding to kill the soil inhabiting pupae has been also recommended. The species is further considered to be a predator of mites. Diagnostic features are listed below according to [[Journal of Integrated Pest Management (2011) 2, I1-I10|Riley et al. (2011)]]. | For control, insecticides are predominantly used. However, temporary flooding to kill the soil inhabiting pupae has been also recommended. The species is further considered to be a predator of mites. Diagnostic features are listed below according to [[Journal of Integrated Pest Management (2011) 2, I1-I10|Riley et al. (2011)]]. | ||
| + | {{BulletedBox|300|Diagnostic features:|two colour forms: pale (yellow with brownish blotches)<br />and dark (dark brown);;antennae with 8 segments;;setae originating along the marginal line connecting<br />the front edges of the two hind ocelli;;pronotal anteromarginal setae shorter<br />than anteroangular setae;;postocular setae IV pronounced;;comb on tergite VIII absent}} | ||
'''Synonyms:'''<br/> | '''Synonyms:'''<br/> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
''Frankliniella lycopersici''<br/> | ''Frankliniella lycopersici''<br/> | ||
''Frankliniella dampfi'' | ''Frankliniella dampfi'' | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 11:24, 24 February 2015
| Literature database |
|---|
| 119 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of natural enemies |
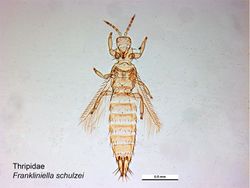
Author(s): Lucinda Gibson, Museum Victoria
Source: PaDIL
Frankliniella schultzei (Trybom 1910) - (yellow flower thrips)
The thrips is widespread in tropical and subtropical regions on buds and flowers of various crops like vegetables and fruit trees. It feeds on the developing shoots, buds and fruits causing dark spots on the leaves and fruit surface, as well as premature drop of flowers and fruits. In addition, it is a vector of several plant viruses, e.g. Tomato spotted wilt virus or Groundnut ringspot virus. Economic damage has been, for example, reported from tomatoes and Capsicum peppers, mainly due to the transmission of viruses.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • English: | yellow flower thrips tomato thrips common blossom thrips |
| • Español: | trips común de las flores |
| • Português: | tripes-do-tomate |
For control, insecticides are predominantly used. However, temporary flooding to kill the soil inhabiting pupae has been also recommended. The species is further considered to be a predator of mites. Diagnostic features are listed below according to Riley et al. (2011).
| Diagnostic features: | |
|---|---|
| • | two colour forms: pale (yellow with brownish blotches) and dark (dark brown) |
| • | antennae with 8 segments |
| • | setae originating along the marginal line connecting the front edges of the two hind ocelli |
| • | pronotal anteromarginal setae shorter than anteroangular setae |
| • | postocular setae IV pronounced |
| • | comb on tergite VIII absent |
Synonyms:
Frankliniella sulphurea
Frankliniella lycopersici
Frankliniella dampfi
- Other images of Frankliniella schultzei (PaDIL - click to enlarge)



