Brome mosaic virus
From Pestinfo-Wiki
| Literature database |
|---|
| 108 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
Brome mosaic virus (BMV)
The virus infects monocots in the Poacea family and some dicots (mainly Chenopodium species). The most commonly infected crops include cereals like barley, wheat, oats or maize. The symptoms are mainly stunting and leaf mosaic. Wheat yield may be reduced by more than 50% (Hodge et al., 2019).
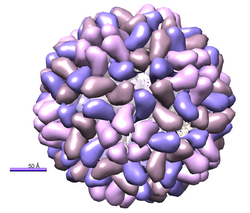
The particles are non-enveloped icosahedrals, 26 nm in diameter, containing 3 positive-sense, capped RNAs, RNA1 to RNA3. Each RNA is enclosed in a separate virion. There is also a subgenomic RNA4 that is expressed from the 3′-end of RNA3 and encodes the coat protein. RNA1 and RNA2 encode proteins used for virus replication and RNA3 the movement protein.
For details see the respective page in Wikipedia.