Aphis glycines
| Literature database |
|---|
| 398 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of natural enemies |
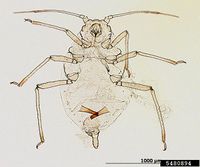
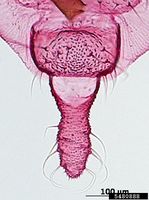
Aphis glycines Matsumura, 1917 - (soybean aphid)
The aphid is native in Asia and has been recorded from North America since 2000. It is a serious pest of soybean and rarely attacks other legume crops. The aphid feeds on the young leaves, petioles and stems, causing yellowing, stunting, reduced pod set and decreased oil content. It is also a vector of various plant viruses like Soybean mosaic virus or Cucumber mosaic virus. Yield losses of up to 40% have been estimated, consisting of direct damage, virus transmission and the buildup of black sooty mold on honeydew produced by the aphid. The arrival of the aphid in North America has dramatically increased the use of pesticides on that crop.
The species overwinters as eggs on its primary host, buckthorn (Rhamnus). The first generation develops on that host. It invades soybean crops during spring where it goes through numerous wingless and parthenogenetic generations. Winged forms of both sexes are produced intermittently and these disperse further when higher population densities have been reached. Eventually it moves back to buckthorn.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Sojalaus |
| • English: | soybean aphid |
| • Español: | áfido de la soya |
| • Français: | puceron du soya |
| • Português: | pulgão-da-soja |
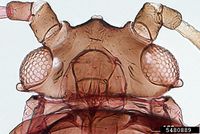
Management involves mainly the use of resistant soybean cultivars. The life cycle of an aphid from birth, through 4 nymphal stages to adult may be as short as 1-2 weeks. Wingless females are green-yellowish and about 1½ mm long. The cornicles, antennae and legs have dark tips. The winged form has a dark thorax.
For further details see
• Tilmon et al., 2011
• Wu et al., 2004
• Wikipedia
- Other images of Aphis glycines (IPM Images - click to enlarge)