Difference between revisions of "Pseudococcus cryptus"
From Pestinfo-Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{TaxLinks|LnkPseudococcus}} |
{{LiteratureDB|{{PAGENAME}}|browse,crops,benefialsN}} | {{LiteratureDB|{{PAGENAME}}|browse,crops,benefialsN}} | ||
[[File:Pseudococcus_cryptus_PaDIL141208a.jpg|250px|thumb|''Pseudococcus cryptus'' (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Author(s): Qing Hai Fan, MAF<br/>Source: [http://www.padil.gov.au/maf-border/Pest/Main/141208 PaDIL]]] | [[File:Pseudococcus_cryptus_PaDIL141208a.jpg|250px|thumb|''Pseudococcus cryptus'' (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Author(s): Qing Hai Fan, MAF<br/>Source: [http://www.padil.gov.au/maf-border/Pest/Main/141208 PaDIL]]] | ||
| − | <font color="#800000">'''''Pseudococcus cryptus'''''</font> Hempel, 1918 - citriculus mealybug | + | <font color="#800000">'''''Pseudococcus cryptus'''''</font> Hempel, 1918 - (citriculus mealybug) |
| − | is | + | |
| + | This mealybug is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions. It infests predominantly citrus, but has been also found on other fruit trees and other crops. The sex pheromone produced by females is known and can be used for capturing males as part of monitoring the populations ([[Applied Entomology and Zoology (2002) 37, 69-72|Arai, 2002]]). | ||
'''Synonyms:'''<br/> | '''Synonyms:'''<br/> | ||
''Pseudococcus citriculus'' | ''Pseudococcus citriculus'' | ||
| + | |||
<gallery widths=200px caption="Other images of Pseudococcus cryptus (PaDIL - click to enlarge)"> | <gallery widths=200px caption="Other images of Pseudococcus cryptus (PaDIL - click to enlarge)"> | ||
Revision as of 10:36, 3 October 2018
| Literature database |
|---|
| 24 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of natural enemies |
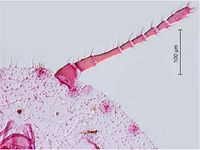
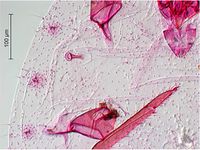
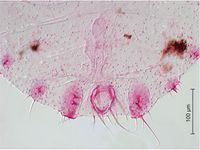
Pseudococcus cryptus Hempel, 1918 - (citriculus mealybug)
This mealybug is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions. It infests predominantly citrus, but has been also found on other fruit trees and other crops. The sex pheromone produced by females is known and can be used for capturing males as part of monitoring the populations (Arai, 2002).
Synonyms:
Pseudococcus citriculus
- Other images of Pseudococcus cryptus (PaDIL - click to enlarge)