Difference between revisions of "Ambrosia artemisiifolia (weed)"
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{TaxLinks|LnkAmbrosiaWeeds}} |
| − | {{ | + | {{LiteratureDBX|{{PAGENAME}}|3131|browse,Ccountrylnk,PaffectedC,AbenefialsN}} |
| − | [[File:Ambrosia_artemisiifolia_IPM5436883.jpg|250px|thumb|''Ambrosia artemisiifolia'' (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Author(s): Bruce Ackley, The Ohio State University<br/>Source: [http://www.ipmimages.org/browse/detail.cfm?imgnum=5436883 IPM Images]]] | + | [[File:Ambrosia_artemisiifolia_IPM5436883.jpg|250px|thumb|''Ambrosia artemisiifolia'' (click on image to enlarge it)<br />Author(s): Bruce Ackley, The Ohio State University<br />Source: [http://www.ipmimages.org/browse/detail.cfm?imgnum=5436883 IPM Images]]] |
| − | <font color="#800000">'''''Ambrosia artemisiifolia'' (weed)'''</font> L. - common ragweed | + | <font color="#800000">'''''Ambrosia artemisiifolia'' (weed)'''</font> L. - (common ragweed) |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The weed is native to North America, but has been accidentally introduced into many other countries, mainly into temperate and subtropical regions. In Europe the first records date back to 1863, but it only became an important weed in that region recently. The weed can be introduced into new areas through contaminated seeds (e.g. cereals and bird seeds), farm machinery or contaminated soil. Common habitats are abandoned land, roadsides, field margins and other disturbed areas. An individual plant produces up to 6000 seeds. The seeds are large and remain viable for more than 30 years. It establishes a long-term persistent seed bank. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ''A. artemisiifolia'' is a serious and competitive annual herbaceous agricultural weed in crops like maize or soybean, causing serious yield losses. For example soybean losses often exceed 50% if the weed is present and no control measures are taken (e.g. [[Agronomy Journal (2018) 110, 646-653|Barnes et al., 2018]]). In addition, it is of special concern as a source of allergies caused by its abundant pollen, produced in late summer and early autumn. Surveys indicate that 10-20% of the population suffers from ''Ambrosia'' allergies in North America and around 5% in Central Europe. In the U.S.A. annual medical costs have been estimated at US$ 3.5 billion in 1997. | ||
{{VN | {{VN | ||
|en=common ragweed<br/>annual ragweed | |en=common ragweed<br/>annual ragweed | ||
| − | |de= | + | |de=beifussblättrige Ambrosie<br />aufrechte Ambrosie<br />beifußblättriges Traubenkraut |
|fr=petite herbe à poux | |fr=petite herbe à poux | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | It grows to a height of 1 m or more. The leaves are deeply divided and may be fern-like. Separate male and female flower-heads are produced on different parts of the same plant. Flowers are abundant, small and inconspicuous. Fruits are also small and contain one seed only, about 2-4 mm long. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Ambrosia artemisiifolia'' var. ''elatior'' (syn. ''Ambrosia elatior'') - annual ragweed. An introduced weed in Hungary and other countries, of South American origin. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Synonyms:'''<br /> | ||
| + | ''Ambrosia elatior'' | ||
| − | |||
<gallery widths=200px caption="Other images of Ambrosia artemisiifolia (weed) (Wikimedia Commons - click to enlarge)"> | <gallery widths=200px caption="Other images of Ambrosia artemisiifolia (weed) (Wikimedia Commons - click to enlarge)"> | ||
Latest revision as of 10:14, 30 March 2022
| Literature database |
|---|
| 427 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • affected crops |
| • list of natural enemies |

Author(s): Bruce Ackley, The Ohio State University
Source: IPM Images
Ambrosia artemisiifolia (weed) L. - (common ragweed)
The weed is native to North America, but has been accidentally introduced into many other countries, mainly into temperate and subtropical regions. In Europe the first records date back to 1863, but it only became an important weed in that region recently. The weed can be introduced into new areas through contaminated seeds (e.g. cereals and bird seeds), farm machinery or contaminated soil. Common habitats are abandoned land, roadsides, field margins and other disturbed areas. An individual plant produces up to 6000 seeds. The seeds are large and remain viable for more than 30 years. It establishes a long-term persistent seed bank.
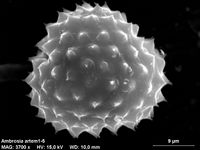
A. artemisiifolia is a serious and competitive annual herbaceous agricultural weed in crops like maize or soybean, causing serious yield losses. For example soybean losses often exceed 50% if the weed is present and no control measures are taken (e.g. Barnes et al., 2018). In addition, it is of special concern as a source of allergies caused by its abundant pollen, produced in late summer and early autumn. Surveys indicate that 10-20% of the population suffers from Ambrosia allergies in North America and around 5% in Central Europe. In the U.S.A. annual medical costs have been estimated at US$ 3.5 billion in 1997.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | beifussblättrige Ambrosie aufrechte Ambrosie beifußblättriges Traubenkraut |
| • English: | common ragweed annual ragweed |
| • Français: | petite herbe à poux |
It grows to a height of 1 m or more. The leaves are deeply divided and may be fern-like. Separate male and female flower-heads are produced on different parts of the same plant. Flowers are abundant, small and inconspicuous. Fruits are also small and contain one seed only, about 2-4 mm long.
Ambrosia artemisiifolia var. elatior (syn. Ambrosia elatior) - annual ragweed. An introduced weed in Hungary and other countries, of South American origin.
Synonyms:
Ambrosia elatior
- Other images of Ambrosia artemisiifolia (weed) (Wikimedia Commons - click to enlarge)