Difference between revisions of "Anarsia lineatella"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{LiteratureDB|{{PAGENAME}}|browse,crops,benefialsN}} | {{LiteratureDB|{{PAGENAME}}|browse,crops,benefialsN}} | ||
[[File:Anarsia lineatella.jpg|250px|thumb|''Anarsia lineatella'' (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Author(s): Donald Hobern<br/>Source: [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Anarsia_lineatella.jpg Wikimedia Commons]]] | [[File:Anarsia lineatella.jpg|250px|thumb|''Anarsia lineatella'' (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Author(s): Donald Hobern<br/>Source: [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Anarsia_lineatella.jpg Wikimedia Commons]]] | ||
| − | <font color="#800000">'''''Anarsia lineatella'''''</font> | + | <font color="#800000">'''''Anarsia lineatella'''''</font> Zeller, 1839 - (peach twig borer) |
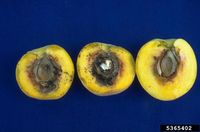
| − | This small moth is native to Europe and sourrounding regions, including parts of North Africa and western Asia. It has been accidentally introduced into North America in the 1880s. ''A. lineatella'' is a serious pest of peach and other stone fruits | + | This small moth is native to Europe and sourrounding regions, including parts of North Africa and western Asia. It has been accidentally introduced into North America in the 1880s. ''A. lineatella'' is a serious pest of peach and other stone fruits. The adults lay eggs on shoots, young leaves or developing fruits. The hatching larvae of the first generation feed on the shoots and often kill them. Fruits are preferred by the later generations and the larvae bore into them, also causing serious damage. |
| + | |||
| + | There are typically 2-3 generations per year, 4 or more in warmer regions. The caterpillars of the last generation overwinter in cracks of the bark. They emerge in spring, feed on the young shoots and pupate in late spring. | ||
{{VN | {{VN | ||
|en=peach twig borer | |en=peach twig borer | ||
Latest revision as of 10:38, 5 January 2019
| Literature database |
|---|
| 38 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of natural enemies |
Anarsia lineatella Zeller, 1839 - (peach twig borer)
This small moth is native to Europe and sourrounding regions, including parts of North Africa and western Asia. It has been accidentally introduced into North America in the 1880s. A. lineatella is a serious pest of peach and other stone fruits. The adults lay eggs on shoots, young leaves or developing fruits. The hatching larvae of the first generation feed on the shoots and often kill them. Fruits are preferred by the later generations and the larvae bore into them, also causing serious damage.
There are typically 2-3 generations per year, 4 or more in warmer regions. The caterpillars of the last generation overwinter in cracks of the bark. They emerge in spring, feed on the young shoots and pupate in late spring.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Pfirsichmotte |
| • English: | peach twig borer |
| • Español: | pequeña minadora de los brotes polilla del melocotonero |
| • Français: | petite mineuse du pêcher mineuse (petite) du pêcher |
- Other images of Anarsia lineatella (IPM Images and PaDIL - click to enlarge)