Difference between revisions of "Thaumetopoea processionea"
From Pestinfo-Wiki
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{TaxLinks|LnkThaumetopoea}} |
| − | {{LiteratureDB|{{PAGENAME}}|browse,benefialsN}} | + | {{LiteratureDB|{{PAGENAME}}|browse,crops,benefialsN}} |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:File by Alexander Baranov - Паровозик (13164983434).jpg|250px|thumb|migrating ''Thaumetopoea processionea'' larvae (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Source: [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:File_by_Alexander_Baranov_-_%D0%9F%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%BE%D0%B7%D0%B8%D0%BA_(13164983434).jpg Wikimedia Commons]]] |
| − | <font color="#800000">'''''Thaumetopoea processionea'''''</font> (Linnaeus, 1758) - oak processionary moth | + | <font color="#800000">'''''Thaumetopoea processionea'''''</font> (Linnaeus, 1758) - (oak processionary moth) |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
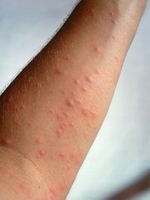
| + | The moth is a defoliator of oak trees in Europe and surrounding regions. Its distribution range extends up to the southern parts of Sweden in the north and to southern parts of Russia and parts of western Asia in the east. Outbreaks can turn into a major health hazard. The barbed and toxic hairs of the caterpillars cause allergic reactions in humans. They break of easily and can become airborne, causing dermatitis as well as pharyngitis when inhaled. | ||
{{VN | {{VN | ||
|en=oak processionary moth | |en=oak processionary moth | ||
|de=[http://www.hortipendium.de/Eichenprozessionsspinner Eichenprozessionsspinner] | |de=[http://www.hortipendium.de/Eichenprozessionsspinner Eichenprozessionsspinner] | ||
| + | |es=procesionaria de la encina | ||
| + | |fr=processionnaire du chêne | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | The nocturnal adult moths have a wingspan of around 3 cm. Control methods include areal spraying of Bt and removing nests using vacuum devices. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For details see the respective page in [[wikipedia:Oak Processionary|Wikipedia]]. | ||
| + | |||
| − | |||
<gallery widths=200px caption="Other images of Thaumetopoea processionea (Wikimedia Commons and IPM Images - click to enlarge)"> | <gallery widths=200px caption="Other images of Thaumetopoea processionea (Wikimedia Commons and IPM Images - click to enlarge)"> | ||
| + | File:Thaumetopoea processionea01.jpg|adult moth | ||
File:Thaumetopoea_processionea_IPM5444411.jpg|eggs | File:Thaumetopoea_processionea_IPM5444411.jpg|eggs | ||
| + | File:Thaumatopoeia.processionea.caterpillar.jpg|caterpillar | ||
File:Thaumetopoea_processionea_IPM2168078.jpg|larvae | File:Thaumetopoea_processionea_IPM2168078.jpg|larvae | ||
File:Thaumetopoea_processionea_IPM5371231.jpg|larvae | File:Thaumetopoea_processionea_IPM5371231.jpg|larvae | ||
Latest revision as of 15:33, 16 July 2018
| Literature database |
|---|
| 32 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of natural enemies |
Thaumetopoea processionea (Linnaeus, 1758) - (oak processionary moth)
The moth is a defoliator of oak trees in Europe and surrounding regions. Its distribution range extends up to the southern parts of Sweden in the north and to southern parts of Russia and parts of western Asia in the east. Outbreaks can turn into a major health hazard. The barbed and toxic hairs of the caterpillars cause allergic reactions in humans. They break of easily and can become airborne, causing dermatitis as well as pharyngitis when inhaled.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Eichenprozessionsspinner |
| • English: | oak processionary moth |
| • Español: | procesionaria de la encina |
| • Français: | processionnaire du chêne |
The nocturnal adult moths have a wingspan of around 3 cm. Control methods include areal spraying of Bt and removing nests using vacuum devices.
For details see the respective page in Wikipedia.
- Other images of Thaumetopoea processionea (Wikimedia Commons and IPM Images - click to enlarge)