Difference between revisions of "Caulimovirus (genus)"
(Redirected page to Category:Caulimovirus (genus)) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{TaxLinks|LnkCaulimoviridae}} | |
| + | {{LiteratureDB|{{PAGENAME}}|browse,crops}} | ||
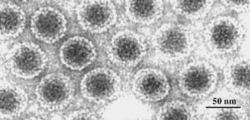
| + | [[File:Virions-Electron micrograph of CaMV virions.png|250px|thumb|electron micrograph of CaMV virions (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Source: [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Virions-Electron_micrograph_of_CaMV_virions.png Wikimedia Commons]]] | ||
| + | <font color="#800000">'''Caulimovirus (genus)'''</font> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Caulimoviruses are similar to the [[Cauliflower mosaic virus|'''Cauli'''flower '''mo'''saic virus]] which is also the most important species of this genus and infects a variety of crops from the family of Brassicaceae. Other species have usually a more restricted host range. The viruses are transmitted by aphids in a semi persistent manner. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Like other [[Caulimoviridae]] and the [[Geminiviridae]] the Caulimoviruses contain double-stranded DNA which is transcribed into RNA before being translated into proteins. During multiplication the transcription is reversed (pararetroviruses). The particles are isometric, not enveloped and 45-50 nm in diameter. The DNA genome contains around 8000 base pairs and encodes 6 or 7 proteins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Currently, the following species have been entered into the system: | ||
| + | {{CategoryMembers3b|Caulimovirus (genus)}} | ||
Revision as of 18:59, 6 June 2015
| Literature database |
|---|
| 180 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
Caulimovirus (genus)
Caulimoviruses are similar to the Cauliflower mosaic virus which is also the most important species of this genus and infects a variety of crops from the family of Brassicaceae. Other species have usually a more restricted host range. The viruses are transmitted by aphids in a semi persistent manner.
Like other Caulimoviridae and the Geminiviridae the Caulimoviruses contain double-stranded DNA which is transcribed into RNA before being translated into proteins. During multiplication the transcription is reversed (pararetroviruses). The particles are isometric, not enveloped and 45-50 nm in diameter. The DNA genome contains around 8000 base pairs and encodes 6 or 7 proteins.
Currently, the following species have been entered into the system: