Pasteuria penetrans (antagonist)
From Pestinfo-Wiki
| Literature database |
|---|
| 138 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • list of pathogens |
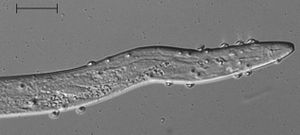
Meloidogyne incognita with endospores of Pasteuria penetrans attached (click on image to enlarge it)
Authors: Victor Phani, Tagginahalli N. Shivakumara, Keith G. Davies and Uma Rao
Source: Frontiers in Microbiology (2017) art. 02122
Authors: Victor Phani, Tagginahalli N. Shivakumara, Keith G. Davies and Uma Rao
Source: Frontiers in Microbiology (2017) art. 02122
Pasteuria penetrans (antagonist) (Thorne, 1940) Sayre & Starr, 1985
The bacterium is a potential, endospore-forming biocontrol agent of Meloidogyne spp. and other species. The spores attach themselves to the cuticle of the 2nd stage juveniles when they search for host roots. After they germinate, the bacteria penetrate the host cuticle and reproduce inside the nematode. The reproduction of females is prevented through the infections. The bacterium is produced commercially and application rates of around 105 endospores/cm3 or 106 endospores/seed can achieve control comparable to that of fumigation treatments (Kokalis-Burelle, 2015).