Melolontha melolontha
| Literature database |
|---|
| 58 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of natural enemies |

Author: Mario Sarto
Source: Wikimedia Commons
Melolontha melolontha (Linnaeus) - (common cockchafer)
The beetle is found in most parts of Europe, but is rare in the Mediterranean region. Damage is mainly done through the larvae - white grubs - which attack pastures and the roots of various crops like potatoes, beets, strawberry, grapevine and vegetables. The adults feed on the leaves of crops and trees. Plants attacked by the larvae wilt and die. Damage can be serious in turf, also sometimes in crops, whereas the related Melolontha hippocastani is more common in forest environments. In contrast to that species outbreaks and crop damage due to M. melolontha have decreased in Central Europe since the 1980s.
The complete life cycle lasts 3 years (sometimes 4 years) and the main adult swarms appear during May and June in these intervals. In historical times, grubs and beetles where manually collected as a control method and then used as food for chicken and pigs. In the 1950s and 1960s, organochlorides, applied to the soil, were widely used.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Feldmaikäfer Gemeiner Maikäfer |
| • English: | common cockchafer European cockchafer |
| • Español: | abejorro común abejorro sanjuanero escarabajo sanjuanero |
| • Français: | hanneton commun |
Currently few chemical pesticides are registered for use against M. melolontha. However, preparations of Beauveria brongniartii for the control of M. melolontha are commercially available.
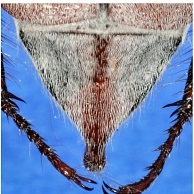
The adult is very similar in size and colouration to M. hippocastani but can be distinguished by the shape and colour of the the male pygidium tip which is longer and lacks a small knob at the end (see illustrations below).
For a review of the biology, damage and control of M. melolontha in the Czech Republic see Muska, 2006.
Synonyms:
Melolontha vulgaris
- Other images of Melolontha melolontha (Wikimedia Commons, IPM Images and PaDIL - click to enlarge)