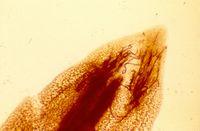
Meloidogyne arenaria
| Literature database |
|---|
| 433 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of antagonists |
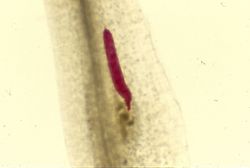
Author: Scot Nelson, Hawaii
Source: Flickr
Meloidogyne arenaria (Neal, 1889) - (peanut root-knot nematode)
The nematode is a serious pathogen which parasitizes many crops and is widespread, especially in warmer regions. For example it is important on groundnuts, tomatoes, green pepper and soybeans. It causes stunting, yellowing and wilting. Yield losses can reach 50% in the field. During warm temperatures, the life-cycle may be as short as 1 month. At the optimum temperature of 27°C, the development time from J2 to egg-laying female lasts about 3 weeks.
Control methods include resistant cutivars, rotation with a non-host crop and nematicides. The female is pear-shaped and white, with a perineal area characterized by a low and flattened dorsal arch. The striae inside the arch form lateral shoulders. Usually, the most reliable identification method is a combination of morphological characters and PCR analysis.
For a summary of the biology see the genus Meloidogyne.
Synonyms:
Heterodera arenaria
Meloidogyne thamesi
- Other images of Meloidogyne arenaria (IPM images and Scot Nelson - click to enlarge)