Gregarina (genus - entomopathogens)
| Literature database |
|---|
| 15 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • list of pest species |
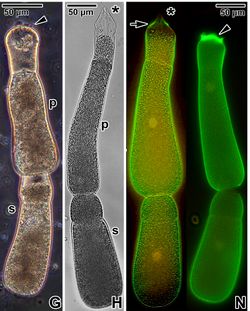
Author: Andrea Valigurová
Source: PLoS ONE (2012), 7(8), art. e42606
Gregarina (entomopathogens) Dufour, 1828
The species of this genus are single-celled gut parasites of various insect groups like beetles, grasshoppers, cockroaches or earwigs. The sporozoites emerging from an ingested oocyst develop into septate trophozoites. The apical part of the trophozoite (the epimerite) becomes embedded in the gut wall while it grows. Mature trophozoites detach themselves again from the gut wall, form a pair with another trophozoite and both transform into a gamont which develops again into an oocyst and is finally excreted by the host.
Species of Gregarina can be very common in some insects, but the impact of the parasites on the host insect has not been frequently studied. However, it is clear that heavy infections can reduce the fitness of the host, by depriving it of nutrients and causing internal malformations. As a consequence, the life span of the insect host can be reduced (Rodriguez et al., 2007).
Type species: Gregarina ovata
Currently, the following species have been entered into the system: