Cactoblastis cactorum
| Literature database |
|---|
| 82 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of natural enemies |

Author(s): Ignacio Baez, USDA Agricultural Research Service
Source: Wikimedia Commons
Cactoblastis cactorum (Berg, 1885) - (cactus moth)
The moth is a pest of prickly pear cacti (Opuntia spp.) in southern North America. It is native to central and north-eastern parts of Argentine, Uruguay and Paraguay. It has been deliberately introduced as a biocontrol agent into several countries to control weedy Opuntia, including the Caribbean in 1957 (see Cactoblastis cactorum - weed bioagent).
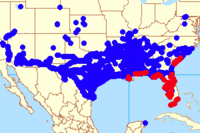
It was first recorded from Florida in 1989 and is considered an important threat to native and endangered Opuntia spp. in the U.S. It is expanding its range reaching South Carolina (2003), Mexico (2006) and Mississippi (2008). Apart from native species, commercially grown Opuntia species are also at risk. Some of these invasions appear to be caused by hurricanes (Andraca-Gómez et al., 2015).
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Kakteenbohrer Kaktusmotte |
| • English: | cactus moth South American cactus moth prickly pear moth |
| • Español: | palomilla del cactus polilla del nopal de América del Sur |
| • Français: | pyrale du cactus |
The larvae are gregarious and feed inside the cactus cladodes. They require about 4 cladodes to complete their development and move on the cactus surface to a new part of the Opuntia plant once a cladode is depleted.
For details see the respective page in Wikipedia.
- Other images of Cactoblastis cactorum (Wikimedia Commons and IPM Images - click to enlarge)