Empoasca fabae
| Literature database |
|---|
| 149 articles sorted by: |
| • year (descending) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of natural enemies |
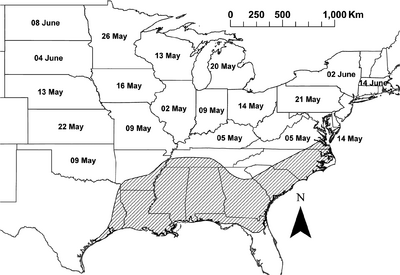
Author(s): Mitchell B. Baker, P. Dilip Venugopal and William O. Lamp
Source: PLoS ONE, 2015, 10 (5) e0124915
Empoasca fabae (Harris, 1841) - (potato leafhopper)
This leafhopper is a serious polyphagous pest of alfalfa, other crops and trees in North America. It feeds and reproduces on over 200 species of plants. It migrates every spring from the Gulf States north to mid-western and north-eastern states and to eastern Canada, with the aid of long-distance southerly winds. It then returns in autumn with northerly winds. Yield losses can reach 50% in these invaded regions. On alfalfa, losses of more than $US 50 per hectare have been estimated around 1990. It has been also reported from western North America.
On alfalfa, damage results in triangular v-shaped yellowing and necrosis at the leaf tips (hopperburn). In soybean, it causes stunting, especially in seedlings. On potato, the damage leads to leaf necrosis and on beans to leaf drop. Control involves monitoring by sweep net and the application of foliar insecticides when the economic threshold has been reached, e.g. an average of 2.5 nymphs per potato leaf. Some alfalfa cultivars (e.g. those with pubescent leaves) have a certain degree of resistance to the pest.
The development from egg, through 5 nymphal stages, to mature adult lasts around 2-4 weeks, depending on the temperature. There may be up to 6 generations per year.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | amerikanische Kartoffelzikade |
| • English: | potato leafhopper |
| • Español: | saltahojas de la papa |
| • Français: | cicadelle de la pomme de terre |
The adult is approximately 3 mm long, yellowish-green with several white markings on the head and notum. Characteristic are the 6 white spots on the pronotum, just behind the head. The wings are transparent and colourless.
For a review see Chasen et al., 2014.
- Other images of Empoasca fabae (IPM Images - click to enlarge)


