Difference between revisions of "Polyphagotarsonemus latus"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
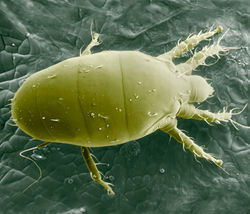
[[File:Polyphagotarsonemus latus, USDA BARC.jpg|250px|thumb|''Polyphagotarsonemus latus'' SEM (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Source: USDA, ARS - [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Polyphagotarsonemus_latus,_USDA_BARC.jpg Wikimedia Commons]]] | [[File:Polyphagotarsonemus latus, USDA BARC.jpg|250px|thumb|''Polyphagotarsonemus latus'' SEM (click on image to enlarge it)<br/>Source: USDA, ARS - [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Polyphagotarsonemus_latus,_USDA_BARC.jpg Wikimedia Commons]]] | ||
<font color="#800000">'''''Polyphagotarsonemus latus'''''</font> (Banks, 1904) - (broad mite)<br/> | <font color="#800000">'''''Polyphagotarsonemus latus'''''</font> (Banks, 1904) - (broad mite)<br/> | ||
| − | is a polyphagous mite | + | is a highly polyphagous mite found in warmer regions and in greenhouses. Damage by the mite was original reported from America and since 1961 also from Europe. It now has a world-wide distribution. The mite attacks the buds of tea, citrus, cotton, ornamentals and other crops by piercing the plant cells and feeding on their content. The attacks result in narrow, curved leaves and deformed fruits. Even relatively low mite densities can result in significant damage. On fruits and ornamentals, the damage is unacceptable for marketing. |
Mites disperse through the air or with infested plant material. For control, predatory mites are used in the greenhouse environment. Alternatively, insecticidal oils or soaps and acaricides are applied. | Mites disperse through the air or with infested plant material. For control, predatory mites are used in the greenhouse environment. Alternatively, insecticidal oils or soaps and acaricides are applied. | ||
| − | |||
{{VN | {{VN | ||
|en=broad mite<br/>yellow tea mite | |en=broad mite<br/>yellow tea mite | ||
Revision as of 19:14, 9 July 2014
Taxonomic position
|
|---|
| Literature database |
|---|
| 102 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of natural enemies |
Polyphagotarsonemus latus (Banks, 1904) - (broad mite)
is a highly polyphagous mite found in warmer regions and in greenhouses. Damage by the mite was original reported from America and since 1961 also from Europe. It now has a world-wide distribution. The mite attacks the buds of tea, citrus, cotton, ornamentals and other crops by piercing the plant cells and feeding on their content. The attacks result in narrow, curved leaves and deformed fruits. Even relatively low mite densities can result in significant damage. On fruits and ornamentals, the damage is unacceptable for marketing.
Mites disperse through the air or with infested plant material. For control, predatory mites are used in the greenhouse environment. Alternatively, insecticidal oils or soaps and acaricides are applied.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Breitmilbe |
| • English: | broad mite yellow tea mite |
| • Español: | acaro amarillo |
| • Français: | tarsoneme du cottonnier |
| • Português: | ácaro-branco |
The adult female is oval in outline and about 0.2-0.3 mm long, light yellowish green in colour. Males are significantly smaller. The development from egg, through the larval and nymphal stages, to the adult stage last around 1-2 weeks depending on the temperature.
- Other images of Polyphagotarsonemus latus (IPM Images and PaDIL - click to enlarge)