Difference between revisions of "Phthorimaea operculella"
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
|pt=traça-da-batatinha | |pt=traça-da-batatinha | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | Pesticides are often used for protecting seed potatoes in the field and fumigation for control of the pest in stored potatoes. In addition, biological means are available like the [[Phthorimaea operculella granulovirus (entomopathogen)|''Phthorimaea operculella'' granulovirus]] or transgenic Bt potatoes resistant to the moth. | ||
| + | |||
The adult is about 1 cm long, grey to brownish with darker spots and small patches on the narrow forewings. | The adult is about 1 cm long, grey to brownish with darker spots and small patches on the narrow forewings. | ||
Revision as of 07:36, 28 April 2014
Taxonomic position
|
|---|
no parent categories |
| Literature database |
|---|
| 214 articles sorted by: |
| • year (recent ones first) |
| • research topics |
| • countries/regions |
| • host plants |
| • list of natural enemies |
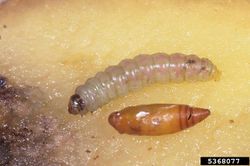
Authors: Merle Shepard, Gerald R.Carner, and P.A.C Ooi (Organization: Insects and their Natural Enemies Associated with Vegetables and Soybean in Southeast Asia)
Source: IPM Images
Phthorimaea operculella (Zeller) - (potato tuber moth)
is an important pest of growing and stored potatoes, tomatoes and other solanaceous crops in warmer regions or of potatoes stored under warmer conditions in temperate countries. It is apparently native to South America, but now has a world-wide distribution. Just one larva can spoil a potato tuber and also introduce fungi during the attack. Losses of stored potatoes can reach 50% or more. Foliage, stems and fruits are also mined and infested. In the field, eggs are laid on the leaves or directly on the tubers if these are close to the surface and in loose soil. The larvae grow to a length of around 1-2 cm, pupate in the soil and might overwinter there. The complete life cycle from egg, over 4 larval stages to mature adult lasts about 4-6 weeks. There may be 6-8 generations per year under suitable conditions. Dispersal is mainly through infested potato tubers.
| Vernacular names | |
|---|---|
| • Deutsch: | Kartoffelmotte |
| • English: | potato tuber moth potato tuberworm tobacco splitworm |
| • Español: | polilla de la patata |
| • Français: | teigne de la pomme de terre |
| • Português: | traça-da-batatinha |
Pesticides are often used for protecting seed potatoes in the field and fumigation for control of the pest in stored potatoes. In addition, biological means are available like the Phthorimaea operculella granulovirus or transgenic Bt potatoes resistant to the moth.
The adult is about 1 cm long, grey to brownish with darker spots and small patches on the narrow forewings.
Synonyms:
Gnorimoschema operculella
- Other images of Phthorimaea operculella (Wikimedia Commons and IPM Images - click to enlarge)

